Azure Virtual Network (VNet): Connecting Networks With Ease
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) revolutionizes network connectivity, offering a seamless solution for businesses to interconnect and streamline operations. Dive into the world of VNet with us.
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) serves as the backbone for secure and efficient communication between various entities within the Azure ecosystem. Let’s explore the intricacies of this pivotal tool.
Overview of Azure Virtual Network (VNet)
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is a service provided by Microsoft Azure that allows you to create isolated networks within the Azure cloud infrastructure. Its primary purpose is to enable you to securely connect Azure resources, such as virtual machines, to each other, the internet, and on-premises networks.
By using Azure Virtual Network, you can benefit from enhanced security, improved network performance, and greater control over your network configuration. Additionally, it allows you to customize your network settings to meet the specific requirements of your applications and workloads.
Benefits of Using Azure Virtual Network
- Securely connect Azure resources: Azure VNet enables you to establish secure connections between virtual machines, web apps, databases, and other Azure services.
- Isolate your network: By creating separate VNets, you can isolate different parts of your infrastructure to enhance security and prevent unauthorized access.
- Extend on-premises networks: Azure VNet allows you to extend your on-premises network to the cloud, enabling seamless communication between your local data center and Azure resources.
- Customize network settings: With Azure VNet, you have full control over IP address ranges, subnets, routing tables, and security policies, allowing you to tailor your network configuration to suit your needs.
Scenarios Where Azure VNet is Useful
- Multi-tier applications: Azure VNet is ideal for deploying multi-tier applications, where different components need to communicate securely while being isolated from each other.
- Hybrid cloud environments: Organizations with hybrid cloud environments can use Azure VNet to establish secure connections between their on-premises infrastructure and Azure resources.
- Internet-facing applications: Azure VNet enables you to securely expose internet-facing applications without compromising security, by implementing network security groups and access control lists.
VNet Architecture
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is a fundamental building block in Azure, allowing you to securely connect Azure resources together. Let’s dive into the architecture of Azure Virtual Network.
Components of Azure Virtual Network
- Address Space: Defines the range of IP addresses that can be used within the VNet.
- Subnets: Divides the VNet into smaller segments for better organization and security.
- Network Security Groups (NSGs): Control inbound and outbound traffic to network interfaces.
- Virtual Network Gateway: Enables secure cross-premises connectivity using VPN or ExpressRoute.
Subnetting Options in Azure Virtual Network
- Subnetting allows you to segment your VNet into smaller networks for better organization and security.
- You can create multiple subnets within a VNet to group resources based on function or security requirements.
- Each subnet can have its own security policies and Network Security Groups (NSGs) for traffic control.
Integration with Other Azure Services
- Azure VNet can integrate seamlessly with other Azure services like Azure Virtual Machines, Azure App Service, and Azure SQL Database.
- This integration allows for secure communication between resources and enables hybrid cloud scenarios.
Creating a Virtual Network in Azure Portal
- Log in to the Azure Portal and navigate to the Virtual Networks blade.
- Click on “Create” and follow the guided steps to configure your VNet, including address space and subnets.
- Review and create your VNet, and you’re all set to start connecting your resources.
Virtual Network vs VPN Gateway in Azure
- A Virtual Network is the foundation that allows you to create isolated networks in Azure, while a VPN Gateway enables secure connectivity to on-premises networks.
- Virtual Network focuses on internal network segmentation and traffic control, whereas VPN Gateway is used for secure cross-premises connections.
Security Features for Azure Virtual Networks
- Network Security Groups (NSGs) provide granular control over inbound and outbound traffic to Azure resources.
- You can define rules in NSGs to allow or deny specific types of traffic based on source, destination, and port.
- NSGs can be associated with subnets or individual network interfaces to control traffic flow within the VNet.
Using Network Security Groups for Traffic Control
- For example, you can create an NSG rule to allow inbound traffic on port 80 to a specific subnet hosting web servers.
- Another rule can block all outbound traffic from a subnet to restrict communication to a particular set of resources.
- By properly configuring NSGs, you can enhance the security posture of your Azure Virtual Network.
VNet Peering
VNet peering allows Azure Virtual Networks to communicate securely with each other by connecting them directly through the Azure backbone network, without the need for a gateway or additional hardware.
Difference between VNet Peering and VNet-to-VNet Connections
- VNet peering is ideal for connecting VNets within the same region, offering low latency and high bandwidth. On the other hand, VNet-to-VNet connections are used to connect VNets across different regions or subscriptions.
- VNet peering does not require a gateway or additional configuration, making it simpler to set up and manage. VNet-to-VNet connections, however, require VPN gateways and specific configurations.
- VNet peering allows for transitive connectivity between peered VNets, enabling communication between multiple VNets through a single peering connection. VNet-to-VNet connections do not support transitive traffic.
Setting Up VNet Peering in Azure Portal
- Go to the Azure Portal and navigate to the Virtual Network blade.
- Select the VNet you want to peer with another VNet and click on “Peerings”.
- Click on “Add” to create a new peering connection.
- Specify the VNet you want to peer with, configure the settings, and complete the peering setup.
- Repeat the process on the other VNet to establish the peering connection.
Limitations of VNet Peering
One important limitation to consider when implementing VNet peering is that transitive peering is not supported across more than one peering connection. Additionally, peered VNets must have non-overlapping address spaces.
Comparison Table: VNet Peering vs. VPN Gateway Connections
| Aspect | VNet Peering | VPN Gateway Connections |
|---|---|---|
| Connectivity | Directly connects VNets within the same region. | Connects VNets across regions or subscriptions. |
| Configuration | Simple setup without the need for a gateway. | Requires VPN gateways and specific configurations. |
| Transitive Traffic | Supports transitive connectivity between peered VNets. | Does not support transitive traffic. |
Network Security in Azure VNet
Azure Virtual Network offers a range of security features to help users secure their virtual networks. One of the key components of network security in Azure VNet is Network Security Groups (NSGs), which play a crucial role in defining and enforcing network security policies.
Network Security Groups (NSGs)
Network Security Groups (NSGs) act as a virtual firewall for controlling inbound and outbound traffic to Azure resources within a VNet. They allow you to filter network traffic based on source and destination IP addresses, port, and protocol. By associating NSGs with subnets or network interfaces, you can create security rules to allow or deny traffic as needed.
- NSG Rules: NSGs consist of security rules that specify the allowed or denied traffic based on defined criteria. These rules can be customized to meet specific security requirements.
- Default Rules: NSGs come with default rules that allow outbound traffic and deny all inbound traffic by default. Users can add custom rules to further secure their network.
- Priority and Order: NSG rules are evaluated based on priority and order, with lower numbers having higher priority. It’s essential to carefully prioritize rules to ensure proper traffic filtering.
Tips for Optimizing Network Security within Azure VNets
When it comes to optimizing network security in Azure VNets, there are some best practices to follow:
- Implement Least Privilege: Restrict network access to only necessary resources by following the principle of least privilege. This helps minimize the attack surface and enhance security.
- Regular Monitoring: Continuously monitor network traffic, security logs, and NSG rules to detect any unusual activity or potential security threats.
- Use Azure Security Center: Leverage Azure Security Center to get security recommendations, threat detection, and security alerts for your Azure resources.
- Enable DDoS Protection: Enable Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Protection Standard to safeguard your Azure resources from DDoS attacks.
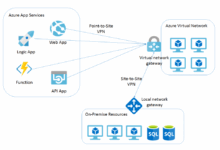
VNet Gateway
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) Gateway plays a crucial role in connecting your on-premises network to your Azure Virtual Network, allowing secure communication between the two environments.
Types of VNet Gateways
- VPN Gateway: Enables secure connections using Virtual Private Network (VPN) technology.
- ExpressRoute Gateway: Provides a dedicated private connection to Azure through Microsoft’s ExpressRoute service.
Configuring and Managing a VNet Gateway
- Configuration: Set up the VNet Gateway through the Azure portal, specifying the gateway type, VPN type, and other necessary settings.
- Connecting Networks: Establish connections between on-premises networks and Azure VNets by configuring the gateway connections.
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting: Monitor the VNet Gateway’s performance and troubleshoot any connectivity issues that may arise.
Network Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Monitoring and troubleshooting network issues within an Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and security.
Tools for Monitoring Network Traffic
- Azure Network Watcher: Provides tools like Network Performance Monitor and Connection Monitor for real-time monitoring and diagnostics.
- Azure Monitor: Offers insights into network performance metrics, logs, and alerts to help identify issues proactively.
- Third-party tools: Utilize third-party monitoring solutions compatible with Azure VNets for additional visibility and analysis.
Common Troubleshooting Techniques
- Check network security groups and rules for any misconfigurations impacting traffic flow.
- Review network interface settings and configurations to ensure proper connectivity.
- Analyze network logs and monitoring data to pinpoint potential bottlenecks or failures.
- Use traceroute and ping tools to test connectivity and identify network latency or packet loss.
Network Performance Optimization Best Practices
- Implement network segmentation to isolate traffic and improve overall network performance.
- Optimize network routing by utilizing Azure Route Tables to define efficient paths for traffic.
- Leverage Azure ExpressRoute for direct connections to Azure data centers, reducing latency and enhancing performance.
- Regularly monitor and analyze network performance metrics to identify areas for improvement and optimization.
Connectivity Options
Implementing connectivity options for Azure VNets involves considering the cost implications, setup process, network bandwidth capabilities, and security features of VPN and ExpressRoute connections.
Cost Implications of VPN vs. ExpressRoute
- VPN connections are generally more cost-effective for small to medium-sized businesses with lower bandwidth requirements.
- ExpressRoute, while more expensive, provides higher reliability, lower latency, and higher throughput for large enterprises with critical workloads.
Setup Process for VPN and ExpressRoute Connections
- VPN Setup: Configure a VPN gateway, create a local network gateway, and establish a connection using the appropriate VPN protocol.
- ExpressRoute Setup: Choose a connectivity provider, select an ExpressRoute circuit type, and establish a connection to the Microsoft network.
Network Bandwidth Capabilities
- VPN Connections: Offer bandwidth ranging from 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps, depending on the VPN gateway SKU.
- ExpressRoute Connections: Provide bandwidth options of 50 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 200 Mbps, 500 Mbps, 1 Gbps, 2 Gbps, 5 Gbps, and 10 Gbps.
Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Connection in Azure
Step-by-step guide:
- Create a virtual network and subnet in Azure.
- Deploy a VPN gateway in the virtual network.
- Configure the local network gateway to represent the on-premises network.
- Establish a connection between the VPN gateway and the local network gateway.
Security Features and Protocols
- VPN Connections: Support protocols such as IPsec and SSTP, with encryption and authentication mechanisms for secure data transmission.
- ExpressRoute Connections: Offer private connectivity to Azure, bypassing the public internet, ensuring data privacy and security.
VNet Integration with On-Premises Networks
Integrating Azure VNets with on-premises networks is crucial for organizations looking to extend their network capabilities to the cloud. This integration allows for seamless connectivity and data exchange between on-premises resources and Azure resources.
VPN Gateways for Connectivity
VPN gateways play a key role in connecting Azure VNets to on-premises networks securely. These gateways establish encrypted tunnels that ensure data transmitted between the two environments is protected from unauthorized access.
- VPN Site-to-Site Connection: This method allows for a secure connection between on-premises VPN devices and Azure VPN gateways, enabling communication between the on-premises network and Azure VNet.
- ExpressRoute: For organizations requiring higher bandwidth and lower latency, ExpressRoute provides a dedicated private connection to Azure, bypassing the public internet for enhanced security and reliability.
Ensuring Secure and Reliable Connectivity
To ensure secure and reliable connectivity between Azure VNets and on-premises networks, consider the following tips:
- Implement Network Security Groups (NSGs) to control inbound and outbound traffic to and from Azure resources.
- Utilize Azure Firewall for advanced threat protection and network security.
- Regularly monitor network traffic and performance to identify and address any connectivity issues promptly.
- Enable multi-factor authentication and strong password policies to secure access to Azure resources.
IP Addressing in Azure VNets
When working with Azure Virtual Networks (VNets), understanding IP addressing is crucial for effectively managing resources and ensuring secure communication within the network.
Subnetting in Azure Virtual Networks
In Azure VNets, subnetting involves dividing the IP address space of a VNet into smaller subnetworks for efficient resource allocation and management. Subnetting influences IP addressing by allowing you to organize resources based on their specific requirements and usage.
Assigning Static and Dynamic IP Addresses
– When assigning IP addresses within a VNet, you can choose between static and dynamic IP addresses. Static IP addresses are manually assigned to resources and remain constant, while dynamic IP addresses are automatically assigned from a pool of available addresses.
– To assign static IP addresses, you can configure the settings directly within the Azure portal or use Azure PowerShell/CLI commands. For dynamic IP addresses, Azure automatically assigns addresses to resources based on the defined settings.
Securing IP Address Spaces in Azure VNets
– Best practices for securing IP address spaces in Azure VNets include defining and enforcing network security rules, using Network Security Groups (NSGs) to control traffic flow based on IP addresses, and regularly monitoring and updating IP address configurations to prevent conflicts.
– By properly configuring NSGs, you can control inbound and outbound traffic to and from resources within the VNet based on specific IP addresses, ports, and protocols. This helps enhance network security and prevent unauthorized access.
Role of Network Security Groups (NSGs)
– Network Security Groups (NSGs) play a crucial role in controlling traffic flow within Azure VNets by acting as a virtual firewall to filter and allow/deny traffic based on IP addresses, ports, and protocols.
– By defining security rules within NSGs, you can restrict access to resources, protect sensitive data, and prevent malicious attacks from compromising the network infrastructure.
Load Balancing in Azure VNets
Load balancing plays a crucial role in Azure Virtual Networks by distributing incoming network traffic across multiple resources to ensure optimal performance, high availability, and reliability.
Types of Load Balancers in Azure
- Azure Load Balancer: Offers low-latency and high-throughput by distributing incoming traffic among healthy instances in Azure VNets.
- Azure Application Gateway: Provides layer 7 load balancing capabilities, allowing for intelligent routing decisions based on application layer data.
Configuring Load Balancing in Azure VNets
- To configure load balancing in Azure VNets, you can create a Basic Load Balancer with a single frontend IP configuration or opt for a Standard Load Balancer for more advanced features and scalability.
- Define load balancing rules to specify how traffic should be distributed among the backend pool of resources.
Performance Impact of Load Balancing Algorithms
- Round Robin: Simple and effective, distributes traffic evenly among backend resources.
- Least Connections: Directs traffic to the server with the fewest active connections, ideal for balancing loads based on current utilization.
Setting up Basic vs. Standard Load Balancer in Azure
- Basic Load Balancer: Suitable for simple scenarios, offering limited features such as inbound NAT rules and load balancing rules.
- Standard Load Balancer: Provides additional capabilities like outbound SNAT, HA ports, and availability zones for enhanced performance and resiliency.
Comparison: Azure Application Gateway vs. Azure Load Balancer
| Features | Azure Application Gateway | Azure Load Balancer |
|---|---|---|
| Layer | Layer 7 (Application) | Layer 4 (Transport) |
| Use Cases | Web traffic routing, SSL termination | Load balancing for VMs, containers |
Troubleshooting Load Balancing Issues in Azure VNets
- Monitor backend health probes to ensure that resources are responding correctly to load balancing requests.
- Check network security group rules to verify that traffic is allowed to flow to and from load balancers.
- Analyze network performance metrics and logs to identify any bottlenecks or connectivity issues affecting load balancing.
Hybrid Cloud Networking
Hybrid cloud networking refers to the integration of on-premises infrastructure with cloud-based resources, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of both environments simultaneously. In the context of Azure VNets, hybrid cloud networking enables seamless connectivity between Azure resources and on-premises systems.
Benefits of Implementing Hybrid Cloud Networking with Azure VNets
- Enhanced Flexibility: Organizations can scale resources up or down based on demand, utilizing both on-premises and cloud infrastructure as needed.
- Cost Efficiency: By optimizing resource usage across on-premises and cloud environments, organizations can reduce operational costs.
- Improved Security: Azure VNets offer secure connectivity options, ensuring data protection and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Disaster Recovery: Hybrid cloud networking allows for the replication of data and applications across multiple locations, enhancing business continuity.
Strategies for Optimizing Network Performance in Hybrid Cloud Environments
- Network Monitoring: Implement robust monitoring tools to track network performance and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Bandwidth Management: Allocate bandwidth effectively between on-premises and cloud resources to ensure optimal performance.
- Traffic Optimization: Utilize traffic management solutions to prioritize critical workloads and enhance overall network efficiency.
- Load Balancing: Implement load balancers to distribute network traffic evenly and prevent overloading of specific resources.
Disaster Recovery and High Availability
In the realm of cloud computing, disaster recovery and high availability are crucial components to ensure business continuity. Azure Virtual Networks (VNets) play a significant role in enabling organizations to design resilient network architectures that can withstand disruptions and maintain continuous operations.
Role of Azure VNets in Disaster Recovery and High Availability
Azure VNets provide the foundation for establishing secure and isolated network environments within the Azure cloud infrastructure. By leveraging VNets, organizations can replicate their on-premises network configurations, ensuring seamless connectivity and data protection in the event of a disaster. In terms of high availability, Azure VNets enable the deployment of redundant network resources across multiple regions to minimize downtime and ensure uninterrupted access to critical applications and services.
Best Practices for Designing Resilient Network Architectures using Azure VNets
- Implementing redundant connections and gateways within Azure VNets to ensure failover capabilities.
- Utilizing Azure Traffic Manager to distribute traffic across multiple regions for high availability.
- Leveraging Azure Site Recovery to automate the replication of virtual machines for disaster recovery purposes.
- Regularly testing disaster recovery procedures to validate the effectiveness of the network architecture.
Examples of Azure VNets Ensuring Business Continuity
Azure VNets can contribute to ensuring business continuity by enabling organizations to establish geographically dispersed network architectures that can withstand localized outages or disasters. For instance, by deploying virtual machines in different Azure regions and connecting them through VNets, organizations can maintain operations even if one region experiences a disruption.
Setting up Azure VNets for Disaster Recovery
To set up Azure VNets for disaster recovery purposes, organizations should:
- Create redundant virtual network gateways for failover capabilities.
- Implement geo-redundant storage for data replication across Azure regions.
- Configure Azure Traffic Manager for load balancing and traffic distribution.
- Leverage Azure Site Recovery for automated VM replication and failover orchestration.
Difference Between Disaster Recovery and High Availability in Azure VNets
Disaster recovery focuses on recovering from catastrophic events, while high availability aims to minimize downtime and ensure continuous operations.
Importance of Subnetting within Azure VNets for Disaster Recovery Planning
Subnetting within Azure VNets allows organizations to segment their network resources and control traffic flow, which is essential for disaster recovery planning. By assigning specific subnets to different applications or services, organizations can prioritize critical workloads during failover scenarios and optimize resource allocation for faster recovery.
Comparison of Azure VNets with Other Azure Services for Achieving High Availability
| Azure VNet Features | High Availability Benefits |
|---|---|
| Redundant Gateway Connections | Ensures failover capabilities for continuous connectivity. |
| Geo-Redundant Storage | Replicates data across Azure regions for data protection. |
| Azure Traffic Manager | Distributes traffic across multiple regions for load balancing and fault tolerance. |
Network Isolation and Segmentation
Network isolation and segmentation are crucial aspects of Azure VNets as they help enhance security, optimize performance, and simplify network management.
Implementing network isolation and segmentation in Azure VNets can be achieved through various methods such as using network security groups (NSGs), virtual network peering, and Azure Firewall. By defining specific rules and policies, organizations can control traffic flow, restrict access to resources, and prevent unauthorized communication between different network segments.
Implementing Network Isolation and Segmentation
- Utilize network security groups (NSGs) to control inbound and outbound traffic based on IP addresses, ports, and protocols.
- Implement virtual network peering to connect multiple VNets securely while keeping traffic isolated within each network.
- Leverage Azure Firewall to centrally manage and enforce security policies across VNets, allowing for deep packet inspection and threat intelligence.
Use Cases for Network Isolation and Segmentation
- Protecting sensitive data: By isolating critical applications and data in a separate network segment, organizations can minimize the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Ensuring compliance: Segregating network resources based on regulatory requirements can help organizations meet industry standards and maintain data privacy.
- Improving performance: Segmenting network traffic can optimize bandwidth usage, reduce latency, and enhance overall network performance for specific applications or services.
Compliance and Governance in Azure VNets
When it comes to Azure Virtual Networks (VNets), compliance and governance play a crucial role in ensuring the security and integrity of network operations. This involves adhering to specific regulatory standards such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) to protect sensitive data and maintain trust with customers.
Configuring Network Security Groups and Access Control Lists
- Network Security Groups (NSGs) and Access Control Lists (ACLs) are essential tools for enforcing governance policies within Azure VNets.
- By configuring NSGs and ACLs, you can control inbound and outbound traffic, restrict access to resources based on IP addresses, ports, and protocols, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Best practices include regularly reviewing and updating NSG rules, implementing least privilege access, and monitoring network traffic to detect and respond to any security incidents.
Monitoring and Auditing Network Traffic
- Monitoring and auditing network traffic is crucial for ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and identifying any unauthorized activities or security breaches.
- By leveraging Azure monitoring tools and services, such as Azure Monitor and Azure Security Center, you can gain visibility into network traffic, detect anomalies, and generate audit reports for compliance purposes.
- Regularly reviewing audit logs, conducting security assessments, and performing penetration testing are recommended practices to maintain a secure and compliant Azure VNet environment.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Implementing Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) in Azure VNets allows you to manage permissions and restrictions effectively by assigning roles to users based on their responsibilities and access requirements.
- RBAC enables you to control who can perform specific actions within the VNet, such as managing virtual machines, configuring network settings, or accessing sensitive data.
- By defining custom roles, monitoring user activities, and enforcing least privilege access, you can enhance governance, mitigate risks, and ensure compliance with regulatory frameworks.
Cost Management for Azure VNets
Azure Virtual Networks (VNets) offer a range of features and capabilities to support various networking needs in the cloud. However, managing costs associated with Azure VNets is a crucial aspect that organizations need to consider in order to optimize their cloud spending effectively.
Cost Implications of Using Azure Virtual Networks
- Azure VNets incur costs based on factors such as the number of resources deployed within the network, data transfer rates, and the use of additional features like VNet Gateway for secure connectivity.
- Increased data transfer between resources within the VNet or between VNets can lead to higher costs, as data transfer pricing is a significant component of Azure networking expenses.
- Implementing high availability and disaster recovery solutions within Azure VNets can also contribute to increased costs due to the usage of redundant resources for failover scenarios.
Optimizing Costs Associated with Azure VNets
- Utilizing reserved instances for virtual machines and other resources within Azure VNets can provide cost savings compared to pay-as-you-go pricing.
- Implementing network security best practices, such as using Network Security Groups (NSGs) effectively to control inbound and outbound traffic, can help reduce costs by preventing unnecessary data transfer.
Monitoring and Controlling Costs in Azure VNets
- Azure Cost Management tools provide visibility into cloud spending and help organizations track their usage and costs associated with Azure VNets.
- Setting budget alerts within Azure Cost Management can enable proactive cost control measures by notifying users when spending thresholds are reached or exceeded.
Impact of VNet Peering and VPN Gateways on Cost Management
- VNet peering allows VNets to communicate with each other directly, which can reduce costs associated with data transfer compared to using VPN gateways for connectivity between separate VNets.
- VPN gateways provide secure connections between on-premises networks and Azure VNets, but they can incur additional costs based on the amount of data transferred and the gateway configuration used.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, Azure Virtual Network (VNet) stands as a robust infrastructure that empowers seamless network integration and security within the Azure environment. Embrace the power of VNet for a connected future.