Azure App Service: Your Gateway To Seamless Application Deployment
Azure App Service sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Dive into the world of effortless application deployment with Azure App Service.
Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting out, Azure App Service provides the tools and features you need to bring your web applications to life. From scalability options to seamless integration with other Azure services, Azure App Service is your go-to platform for deploying applications with ease.
Overview of Azure App Service
Azure App Service is a fully managed platform-as-a-service (PaaS) offering from Microsoft Azure that allows developers to build, deploy, and scale web applications and APIs quickly and easily. It provides a seamless experience for managing applications without worrying about infrastructure management.
Purpose of Azure App Service
Azure App Service simplifies the process of deploying and managing web applications, enabling developers to focus on building great apps without the overhead of infrastructure management. It supports multiple programming languages, frameworks, and tools, making it versatile for various development needs.
Key Features of Azure App Service
- Automatic scaling based on demand
- Continuous deployment from Git, GitHub, Azure DevOps, or other sources
- Built-in monitoring and diagnostics
- Integration with Azure Active Directory for authentication
- Support for multiple deployment slots for staging and production environments
Examples of Applications Using Azure App Service
Azure App Service can be used to deploy various types of applications, such as e-commerce websites, content management systems, customer portals, and RESTful APIs.
Scalability Options with Azure App Service
Azure App Service offers horizontal and vertical scaling options to handle increased traffic or workload demands. It can automatically scale based on predefined metrics or manually adjusted to meet specific requirements.
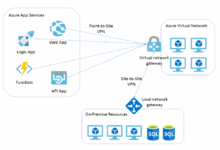
Integration with Other Azure Services
Azure App Service seamlessly integrates with other Azure services like Azure SQL Database, Azure Cosmos DB, Azure Functions, and Azure Storage for enhanced functionality and capabilities in building modern cloud applications.
Pricing Structure for Azure App Service
Azure App Service offers different pricing tiers based on the resources and features required, such as Free, Shared, Basic, Standard, Premium, and Isolated. Pricing is based on usage and additional features like custom domains, SSL certificates, and auto-scaling.
Comparison with Other Cloud Providers
Azure App Service competes with similar services like AWS Elastic Beanstalk and Google App Engine, offering a robust platform with integrated development tools, scalability options, and seamless integration with other Azure services.
Deploying a Simple Web Application with Azure App Service
- Create an Azure account and navigate to the Azure portal
- Create a new App Service and configure the required settings
- Deploy your web application code using FTP, Git, or Azure DevOps
- Configure custom domains, SSL certificates, and scaling options as needed
- Monitor and manage your web application through the Azure portal
Creating and Deploying Applications
Creating and deploying applications on Azure App Service is a straightforward process that involves a few key steps. Let’s walk through how to create a new app, deploy it to Azure App Service, discuss integration options with source control systems, and share best practices for deployment.
Creating a New App in Azure App Service
When creating a new app in Azure App Service, follow these steps:
- Create a new resource in the Azure portal and select App Service as the type.
- Choose a unique name for your app, select the appropriate subscription, resource group, and App Service plan.
- Configure any additional settings such as runtime stack, operating system, and region.
- Once the app is created, you can start developing and uploading your application code.
Deploying an Application to Azure App Service
To deploy an application to Azure App Service, you can follow these steps:
- Choose the deployment method that suits your needs – FTP, Git, Azure DevOps, or containers.
- Connect your chosen deployment method to your Azure App Service instance.
- Upload your application code or container image through the selected deployment method.
- Monitor the deployment process and verify that your application is running successfully.
Integration Options with Source Control Systems
Azure App Service offers seamless integration with popular source control systems like GitHub, Azure DevOps, and Bitbucket for deployment. This allows you to automatically deploy your application whenever you push changes to your repository.
Best Practices for Deploying Applications on Azure App Service
When deploying applications on Azure App Service, consider the following best practices:
- Use deployment slots to deploy updates without affecting the production environment.
- Enable auto-scaling to handle fluctuations in traffic and ensure optimal performance.
- Monitor application performance and set up alerts to proactively address any issues.
- Leverage Azure DevOps pipelines for automated testing and deployment to streamline the process.
Managing App Service Plans
An App Service plan in the context of Azure is essentially a set of resources used to run applications within Azure App Service. It determines the location, features, and capacity of the App Service apps that you deploy.
Comparing Pricing Tiers for App Service Plans
Different pricing tiers for App Service plans offer varying levels of features and performance, catering to different needs and budgets. Here is a comparison of some common pricing tiers:
- Free Tier: Ideal for testing and small applications with limited resources.
- Shared Tier: Suitable for small applications with fewer features and resources.
- Basic Tier: Offers more features and resources for production applications with moderate traffic.
- Standard Tier: Provides enhanced features and resources for larger production applications.
- Premium Tier: Designed for high-performance applications with advanced features and resources.
Scaling an App Service Plan
Scaling an App Service plan can be done by scaling up (increasing resources) or scaling out (increasing instances). Here’s how you can do it:
- Scaling Up: Navigate to the Azure portal, select your App Service plan, and choose a higher pricing tier with more resources.
- Scaling Out: Increase the instance count in the Scale Out section of your App Service plan settings.
Impact of Scaling on Performance and Cost
Scaling up can improve performance by providing more resources, but it may increase costs. Scaling out can enhance performance by distributing load, but it also incurs additional costs for each instance.
Configuring Auto-Scaling for an App Service Plan
To configure auto-scaling based on predefined performance metrics, follow these steps:
- Go to your App Service plan settings in the Azure portal.
- Select Scale Out (App Service Plan) and enable Auto Scale.
- Set up rules based on metrics like CPU percentage, memory usage, or HTTP queue length.
- Define minimum and maximum instance counts to automatically adjust based on workload.
Setting Up Custom Domains for App Service Plans
Setting up custom domains for different App Service plans involves configuring DNS records to point to your Azure App Service. This can be done through the Azure portal by adding custom domains to your App Service.
Integrating Azure Monitor with an App Service Plan
To effectively monitor performance and resource usage, you can integrate Azure Monitor with an App Service plan by following these steps:
- Access the Azure Monitor section in the Azure portal.
- Select the specific metrics and logs you want to monitor for your App Service plan.
- Set up alerts and notifications based on thresholds to stay informed about performance issues.
Monitoring and Diagnostics
Monitoring and diagnostics are crucial aspects of maintaining the health and performance of Azure App Service applications. By effectively monitoring and diagnosing issues, you can ensure that your applications are running smoothly and efficiently. In this section, we will explore the monitoring capabilities available for Azure App Service, setting up alerts, using diagnostic tools, best practices for monitoring and maintaining applications, creating custom metrics, configuring alerts in Azure Monitor, using Log Analytics for performance analysis, and optimizing monitoring configurations.
Monitoring Capabilities
- Azure Monitor provides a comprehensive set of monitoring tools for Azure App Service, allowing you to track performance, availability, and usage metrics.
- You can view real-time metrics, logs, and traces to monitor the health of your applications and detect any issues promptly.
- Integration with Application Insights enables deeper insights into application performance, dependencies, and user behavior.
Setting Up Alerts
- Configure alerts in Azure Monitor to receive notifications when specific conditions are met, such as high CPU usage or application errors.
- Define alert rules based on metrics thresholds, and choose notification channels like email, SMS, or webhook to stay informed about critical events.
Diagnostic Tools
- Use diagnostic tools like Application Insights and Azure Log Analytics to troubleshoot issues by analyzing logs, performance data, and dependencies.
- Identify bottlenecks, errors, and performance degradation to optimize application performance and user experience.
Best Practices
- Regularly review and adjust monitoring configurations to ensure they align with application requirements and performance goals.
- Monitor key metrics related to application performance, response times, resource utilization, and user interactions.
- Implement automated monitoring and alerting to proactively identify and address issues before they impact users.
Creating Custom Metrics
- Define custom metrics in Azure Monitor to track specific performance indicators that are relevant to your applications.
- Use custom metrics to monitor unique aspects of your applications and gain insights tailored to your specific use cases.
Alert Configuration in Azure Monitor
- Configure different types of alerts in Azure Monitor, such as metric alerts, activity log alerts, and log alerts, to monitor various aspects of your App Service applications.
- Customize alert conditions, thresholds, and actions to ensure timely notifications and effective response to critical events.
Using Log Analytics for Performance Analysis
- Utilize Log Analytics to collect, analyze, and visualize log data from Azure App Service applications for performance tuning and issue resolution.
- Query log data to identify trends, anomalies, and patterns that impact application performance, and take necessary actions to optimize performance.
Optimizing Monitoring Configurations
- Optimize monitoring configurations by adjusting sampling rates, retention periods, and alert thresholds to balance cost-effectiveness and monitoring efficiency.
- Leverage features like autoscaling and dynamic scaling to adapt monitoring resources to application workload changes and reduce unnecessary monitoring overhead.
Integration with Azure Services
Azure App Service offers seamless integration with various Azure services to enhance application functionality and performance. Let’s explore the different Azure services that can be integrated with Azure App Service and how to set up and configure these integrations.
Azure Services Integration
- Azure Functions: Easily run small pieces of code in the cloud without managing servers. Integration with Azure App Service allows for event-driven scenarios and serverless computing.
- Azure SQL Database: Provides a fully managed relational database service. Integration with Azure App Service allows for storing and retrieving data efficiently for web applications.
- Azure Blob Storage: Scalable object storage for unstructured data. Integration with Azure App Service enables storing and accessing files, images, and other content for web applications.
Benefits of Integration
- Enhanced scalability and flexibility for applications.
- Improved performance and reliability by leveraging specialized Azure services.
- Streamlined development and deployment processes through seamless integration.
Setting Up Integrations
- Access the Azure portal and navigate to the Azure App Service you want to integrate with.
- Go to the “Settings” tab and select “Configuration.”
- Add the connection string or configuration details for the desired Azure service.
- Save the changes and restart the Azure App Service for the integration to take effect.
Troubleshooting Integration Issues
Common issues during integration may include incorrect connection strings, permission settings, or network configurations. To troubleshoot, double-check the configuration details, check for any error messages, and ensure proper permissions are set.
Comparison Table of Azure Services
| Azure Service | Key Features | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Azure Functions | Serverless computing, event-driven scenarios | Automated tasks, data processing |
| Azure SQL Database | Fully managed relational database | Data storage, retrieval for web applications |
| Azure Blob Storage | Scalable object storage | File storage, content management for web apps |
Security and Compliance
When it comes to security and compliance in Azure App Service, there are several key features and best practices to consider to ensure the safety of your applications and data.
Security Features in Azure App Service
- Azure Web Application Firewall: Helps protect your web applications from common web vulnerabilities.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Allows you to control access to resources based on roles assigned to users.
- Network Security Groups: Enables you to filter network traffic to and from Azure resources.
- Encryption at Rest: Data stored in Azure App Service is encrypted to protect sensitive information.
Best Practices for Securing Applications
- Implement secure coding practices to prevent common vulnerabilities like SQL injection and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS).
- Regularly update and patch your applications and dependencies to address any security vulnerabilities.
- Enable multi-factor authentication for added security when accessing your Azure App Service resources.
- Monitor and audit your applications for any suspicious activity or security breaches.
Compliance Certifications and Standards
- Azure App Service is compliant with various industry standards such as ISO 27001, SOC 1 and SOC 2, HIPAA, and GDPR.
- These certifications ensure that Azure App Service meets strict security and compliance requirements for handling sensitive data.
Configuring SSL Certificates
- To configure SSL certificates for secure connections in Azure App Service, you can either upload your own certificate or use a certificate provided by Azure.
- Ensure that your SSL certificate is up to date and valid to maintain secure communication between your applications and users.
Custom Domains and SSL
Setting up a custom domain for an Azure App Service application involves specific configurations in the Azure portal. Custom domains help establish a unique identity for your application and enhance brand recognition.
Types of SSL Certificates
- Self-Signed SSL Certificates: Typically used for development and testing purposes, but not recommended for production environments due to security risks.
- Domain Validated (DV) SSL Certificates: Verify domain ownership only, providing basic encryption for data transfer.
- Organization Validated (OV) SSL Certificates: Verify domain ownership and organization details, offering a higher level of trust and security.
- Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates: Most secure option, validating domain ownership, organization details, and legal existence, displaying a green address bar in browsers.
Obtaining and Configuring SSL Certificates
To obtain an SSL certificate, you can either purchase one from a Certificate Authority (CA) or use a free option like Let’s Encrypt. Once obtained, configure SSL bindings in Azure App Service by uploading the certificate and setting up bindings for the custom domain. Follow security best practices and ensure the certificate is up-to-date to maintain a secure connection.
Monitoring and Renewing SSL Certificates
Regularly monitor SSL certificates for expiration dates and renew them before they expire to avoid service disruptions. Implement automated processes for certificate renewal to streamline the management of multiple custom domains within Azure App Service. Keep track of certificate validity and take proactive measures to prevent any security issues.
Continuous Deployment
Continuous deployment is a software development practice where code changes are automatically built, tested, and deployed to production environments. This approach allows teams to release updates frequently, reducing the time between writing code and delivering it to users. In the context of Azure App Service, continuous deployment streamlines the process of updating applications hosted on the platform, ensuring rapid and efficient delivery of new features and bug fixes.
Setting up Continuous Deployment Pipelines
Setting up continuous deployment pipelines for Azure App Service apps using Azure DevOps involves creating a release pipeline that automates the deployment process. This can be achieved by integrating Azure DevOps with Azure App Service, configuring the deployment triggers, and defining the deployment tasks. By linking the source code repository to the deployment pipeline, any changes pushed to the repository can trigger automatic builds and deployments to the Azure App Service environment.
- Integrate Azure DevOps with Azure App Service.
- Configure deployment triggers and deployment tasks in the release pipeline.
- Link the source code repository to the deployment pipeline for automatic deployments.
Configuring Webhooks for Automatic Deployments
Webhooks are a mechanism for triggering automated actions in response to events. Configuring webhooks for Azure App Service allows deployments to be automatically triggered when specific events occur, such as code commits or pull requests. By setting up webhooks, developers can streamline the deployment process and ensure that updates are deployed promptly and consistently.
- Create a webhook in Azure App Service linked to the source code repository.
- Define the events that should trigger the webhook, such as code pushes or pull requests.
- Configure the webhook to call the deployment pipeline in Azure DevOps for automatic deployments.
Importance of Version Control Systems
Version control systems like Git play a crucial role in successful continuous deployment by enabling teams to track changes, collaborate on code, and maintain a history of revisions. By using Git repositories to manage code, developers can ensure that updates are versioned, tested, and deployed reliably. This ensures that deployments are consistent, rollback is possible if needed, and changes are traceable throughout the development lifecycle.
- Track changes and revisions in the codebase using version control systems like Git.
- Collaborate effectively on code with team members using Git repositories.
- Maintain a history of code changes for audit trails and troubleshooting purposes.
Advantages of Using Docker Containers
Using Docker containers in continuous deployment offers several advantages over traditional deployment methods. Containers provide a lightweight, portable, and consistent environment for deploying applications, ensuring that dependencies are bundled with the application code. This simplifies deployment and scalability, enables faster deployment times, and enhances the overall reliability and consistency of the deployment process.
- Isolate application dependencies within Docker containers for consistency and portability.
- Facilitate rapid deployment and scaling of applications using containerization.
- Enhance reliability and consistency of deployments by packaging applications with their dependencies.
Case Study: Successful Implementation of Continuous Deployment
In a real-world Azure App Service project, a software development team implemented continuous deployment practices to streamline the release process and improve delivery efficiency. By setting up automated deployment pipelines using Azure DevOps, configuring webhooks for automatic deployments, and leveraging version control systems like Git, the team achieved faster release cycles, reduced manual errors, and increased overall productivity. The use of Docker containers further enhanced deployment speed and reliability, allowing the team to deliver updates to production environments seamlessly.
Performance Optimization
Optimizing the performance of applications running on Azure App Service is crucial for ensuring a seamless user experience. By employing various techniques and strategies, you can enhance the efficiency and responsiveness of your applications.
Techniques for Optimization
- Utilize caching mechanisms to store frequently accessed data and reduce the need for repeated database queries.
- Implement asynchronous programming to allow tasks to run concurrently and improve overall application speed.
- Optimize database queries by indexing tables, eliminating unnecessary joins, and minimizing data retrieval.
- Utilize content delivery networks (CDNs) to distribute content closer to end-users and reduce latency.
Monitoring and Analysis
- Use Azure Monitor to track performance metrics, identify bottlenecks, and troubleshoot issues in real-time.
- Leverage Application Insights to gain deep insights into application performance, user interactions, and dependencies.
- Set up alerts and notifications to proactively address performance issues before they impact users.
Improving Response Times and Latency
- Optimize code by reducing unnecessary computations, minimizing input/output operations, and eliminating bottlenecks.
- Utilize Azure Traffic Manager to route users to the nearest data center for faster response times.
- Implement load balancing to distribute incoming traffic evenly across multiple instances and improve responsiveness.
Optimizing Resource Utilization
- Scale your Azure App Service instances based on demand to ensure optimal resource allocation and cost-efficiency.
- Configure auto-scaling rules to automatically adjust resources according to predefined thresholds and performance metrics.
- Monitor resource consumption and adjust settings accordingly to prevent resource wastage and optimize performance.
High Availability and Disaster Recovery
High availability and disaster recovery are crucial aspects of ensuring the reliability and continuity of your applications hosted on Azure App Service. Let’s delve into the key features and strategies to maintain high availability and recover from disasters effectively.
High Availability Features in Azure App Service
- Azure App Service provides built-in load balancing and automatic OS patching to ensure high availability of your applications.
- Deployment slots enable seamless swapping of production and staging environments to minimize downtime during updates.
- Integration with Azure Traffic Manager allows for distribution of incoming traffic across multiple regions for increased availability.
Configuring Auto-Scaling for High Availability
- Auto-scaling in Azure App Service can be configured based on metrics like CPU usage or requests per second to ensure optimal performance during peak loads.
- By setting up auto-scaling rules, the platform can automatically adjust the number of instances to meet demand, enhancing availability and responsiveness.
Disaster Recovery Strategies
- Implementing geo-redundant storage ensures that your data is replicated across different Azure regions, protecting against data loss in case of a disaster.
- Setting up Azure Backup or Azure Site Recovery provides options for backing up and recovering your applications and data in the event of a catastrophe.
Monitoring and Alerting Mechanisms
- Utilizing Azure Monitor and Application Insights helps in monitoring the health and performance of your applications, enabling proactive identification of issues that may impact availability.
- Configuring alerts based on specific metrics allows for timely notifications and remediation actions to maintain high availability and mitigate potential disasters.
Comparing Azure Backup and Azure Site Recovery
- Azure Backup focuses on data protection and recovery, while Azure Site Recovery offers comprehensive disaster recovery solutions for virtual machines and applications.
- Choosing between the two services depends on the specific requirements of your organization in terms of data backup, recovery time objectives (RTO), and recovery point objectives (RPO).
SLAs for High Availability and Disaster Recovery
- Azure App Service guarantees a high availability SLA of 99.95%, ensuring that your applications are accessible and operational with minimal downtime.
- For disaster recovery, Azure offers SLAs for services like Azure Backup and Azure Site Recovery, outlining the level of support and uptime commitment in case of a disaster.
Container Deployment
Containerization is a method of packaging an application along with its dependencies, configurations, and runtime environment into a single unit known as a container. This allows the application to run consistently across different environments, making it easier to deploy and manage applications efficiently.
Deploying Containerized Applications to Azure App Service
When deploying containerized applications to Azure App Service, you can use Azure Container Registry to store and manage container images. You can then deploy these container images to Azure App Service using Azure portal, Azure CLI, or Azure DevOps.
Differences Between Traditional and Containerized Apps Deployment
- Traditional apps are deployed by uploading the application code directly to Azure App Service, while containerized apps are deployed as container images.
- Containerized apps offer more flexibility and consistency in deployment, as they encapsulate all dependencies and configurations within the container.
- Containerized apps allow for easier scaling and portability compared to traditional apps.
Advantages of Container Deployment for Azure App Service
- Improved application isolation and security, as containers run independently from each other.
- Efficient resource utilization, as containers share the same OS kernel and only require the resources they need to run.
- Easy scalability and portability, allowing for seamless deployment across different environments.
- Simplified deployment process, as container images can be easily managed and updated without affecting the underlying infrastructure.
Compliance and Governance
When it comes to Azure App Service, compliance and governance are crucial aspects that organizations need to consider. Ensuring that the service meets the necessary standards and regulations is essential for maintaining data privacy and security.
Compliance Standards and Regulations
- Azure App Service complies with various industry standards and regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, ISO, and SOC.
- These standards ensure that data processed and stored within Azure App Service meets the required security and privacy protocols.
- Organizations can leverage Azure’s compliance certifications to demonstrate their adherence to these regulations.
Meeting Compliance Requirements
- Azure App Service provides built-in security features and compliance controls to help organizations meet their regulatory requirements.
- Organizations can configure settings within Azure App Service to align with specific compliance standards.
- Regular audits and monitoring tools in Azure App Service assist in maintaining compliance and governance.
Governance Best Practices
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to manage permissions and access to Azure App Service resources.
- Establish clear policies and procedures for resource management, deployment, and monitoring within Azure App Service.
- Regularly review and update governance policies to adapt to changing compliance requirements.
Data Privacy and Security Tips
- Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit to ensure data privacy within Azure App Service.
- Implement multi-factor authentication for enhanced security when accessing Azure App Service resources.
- Regularly monitor and audit access to data within Azure App Service to prevent unauthorized activity.
Cost Management
When using Azure App Service, understanding the cost structure is essential to optimize expenses and manage your budget effectively.
Cost Structure of Azure App Service
- Azure App Service offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, where you only pay for the resources you use.
- Costs are based on factors such as the number of instances, storage, data transfer, and additional features like custom domains or SSL certificates.
- There are different pricing tiers available, ranging from Free and Shared plans to Premium and Isolated plans with varying capabilities and costs.
Optimizing Costs on Azure App Service
- Rightsize your App Service plan by selecting the appropriate tier and instance size based on your application’s requirements.
- Utilize auto-scaling to automatically adjust the number of instances based on workload, optimizing resource usage and reducing costs during low traffic periods.
- Implement caching mechanisms to reduce database calls and improve performance, ultimately lowering costs associated with data transfer and storage.
Cost Management Tools and Techniques
- Use Azure Cost Management + Billing to monitor and analyze your Azure spending, set budgets, and receive alerts for cost overruns.
- Leverage Azure Advisor to get personalized recommendations for optimizing your resources and reducing costs.
- Implement tagging to track and allocate costs more effectively across different departments or projects within your organization.
Strategies for Reducing Costs
- Regularly review and optimize your Azure App Service usage to identify and eliminate any unused or underutilized resources.
- Consider reserved instances or prepay options for cost savings and discounts on long-term commitments.
- Implement serverless computing with Azure Functions to run code without provisioning or managing servers, reducing operational costs.
Last Word
In conclusion, Azure App Service opens up a world of possibilities for developers looking to streamline their application deployment processes. With its robust features, seamless integrations, and cost-effective pricing tiers, Azure App Service is the ultimate solution for all your application deployment needs.