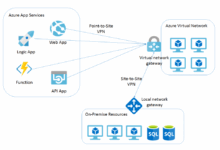
Azure App Service: Your Ultimate Guide To Application Deployment
Azure App Service offers a comprehensive platform for hosting web applications, REST APIs, and mobile backends. Dive into this guide to explore its key features, deployment process, scaling options, and much more.
Overview of Azure App Service
Azure App Service is a cloud-based platform offered by Microsoft Azure that allows developers to build, deploy, and scale web applications, REST APIs, and mobile backends easily. Some key features of Azure App Service include seamless integration with other Azure services, auto-scaling capabilities, and built-in security features. By leveraging Azure App Service, developers can focus on building their applications without worrying about infrastructure management.
Deployment Process on Azure App Service
- Access the Azure Portal and navigate to the Azure App Service resource.
- Upload your web application code or container image to Azure App Service.
- Configure application settings, connection strings, and other parameters as needed.
- Choose the appropriate pricing tier and scaling options for your application.
- Click on the “Deploy” button to launch your web application on Azure App Service.
Scaling Options in Azure App Service
- Azure App Service offers various scaling options such as manual scaling, auto-scaling based on metrics, and reserved instances.
- Manual scaling allows you to manually adjust the number of instances running your application.
- Auto-scaling based on metrics automatically adjusts the number of instances based on predefined thresholds.
- Reserved instances provide cost savings for applications with predictable traffic patterns.
Custom Domain Configuration in Azure App Service
- To set up a custom domain, add a CNAME record pointing to the Azure App Service domain.
- Configure SSL certificates to enable secure communication over custom domains.
- Common issues with custom domain configuration include DNS propagation delays and certificate mismatches.
Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD) with Azure App Service
- Implementing CI/CD pipelines with Azure App Service automates the build, test, and deployment processes, improving efficiency and reliability.
- Set up a CI/CD pipeline using Azure DevOps or GitHub Actions to streamline development workflows.
- Integrating CI/CD workflows seamlessly with Azure App Service ensures continuous delivery of updates to your application.
Setting up Azure App Service
Setting up Azure App Service is a crucial step in deploying your web applications to the cloud. This process involves creating an instance of Azure App Service, configuring its settings, and optimizing it for performance.
Creating an Azure App Service Instance
To create an Azure App Service instance, follow these steps:
- Log in to the Azure Portal.
- Click on “Create a resource” and search for “App Service” in the Marketplace.
- Select the desired subscription, resource group, and region for your App Service instance.
- Provide a unique name for your App Service, choose the runtime stack, and configure other settings as needed.
- Click on “Review + create” and then “Create” to provision your Azure App Service instance.
Configuring Settings for Azure App Service
To configure the settings for your Azure App Service, you can:
- Set up custom domains for your web applications.
- Configure scaling options to handle varying levels of traffic.
- Enable continuous deployment to automatically deploy updates from your chosen source control repository.
- Manage SSL certificates for secure connections to your web applications.
Best Practices for Optimal Performance
To ensure optimal performance of your Azure App Service, consider the following best practices:
- Use Azure Traffic Manager to distribute traffic across multiple Azure App Service instances for high availability.
- Implement caching mechanisms to improve the speed and responsiveness of your web applications.
- Monitor the performance of your Azure App Service using Azure Monitor to identify and address any bottlenecks.
- Regularly update and optimize your web applications to leverage the latest features and improvements offered by Azure App Service.
Deployment options in Azure App Service
Azure App Service offers various deployment options to streamline the process of deploying applications to the cloud. Understanding the different options available can help you choose the most suitable method for your specific needs.
Deployment via Azure Portal
- Deploying applications through the Azure Portal is user-friendly and straightforward.
- Simply navigate to your Azure App Service resource, select the “Deployment Center,” and follow the on-screen instructions to deploy your application.
- Advantages:
- Intuitive interface for quick deployment.
- Easy to monitor and manage deployments directly from the Azure Portal.
- Disadvantages:
- May not be suitable for complex deployment scenarios that require more customization.
Deployment via Git
- Deploying applications using Git provides version control and seamless integration with source control repositories like GitHub.
- Connect your Azure App Service to your Git repository, set up continuous integration, and automatically deploy updates whenever code changes are pushed.
- Advantages:
- Automated deployment process for efficient updates.
- Supports collaboration and team development through version control.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires knowledge of Git and source control concepts.
- Limited customization options compared to other deployment methods.
Deployment via Azure DevOps
- Utilizing Azure DevOps for deployment offers a comprehensive solution for building, testing, and deploying applications.
- Create pipelines in Azure DevOps to automate the deployment process and ensure consistent delivery of updates.
- Advantages:
- End-to-end integration for development and deployment workflows.
- Advanced features for testing, monitoring, and reporting.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires additional configuration and setup compared to other deployment methods.
- May involve a learning curve for users unfamiliar with Azure DevOps.
Scaling in Azure App Service
Scaling in Azure App Service refers to the ability to adjust the resources allocated to your application based on its demand. This ensures that your application can handle varying levels of traffic efficiently.
Different Scaling Options in Azure App Service
- Vertical Scaling: Also known as scaling up, this option involves increasing the resources, such as CPU and RAM, of the existing server. It allows for better performance but may have limitations based on the hardware capacity.
- Horizontal Scaling: Also known as scaling out, this option involves adding more instances of the application to distribute the load. It provides better scalability and availability by spreading the workload across multiple servers.
Factors to Consider for Scaling Strategy
- Expected Traffic: Analyze the expected traffic patterns to determine the appropriate scaling method.
- Cost: Consider the cost implications of each scaling option to ensure cost-effectiveness.
- Performance Requirements: Evaluate the performance requirements of your application to choose the right scaling strategy.
Manual Scaling in Azure App Service
To manually scale an Azure App Service plan, follow these steps:
- Go to the Azure Portal and navigate to the App Service Plan you want to scale.
- Click on the “Scale Up” or “Scale Out” option, depending on whether you want to vertically or horizontally scale.
- Select the desired pricing tier or instance count based on your requirements.
- Click on the “Apply” button to save the changes.
Difference Between Horizontal and Vertical Scaling
Horizontal scaling adds more instances to handle the load, while vertical scaling increases the resources of the existing instance.
Manual Scaling vs. Autoscaling Comparison Table
| Aspect | Manual Scaling | Autoscaling |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Provides full control over resource allocation. | Automatically adjusts resources based on predefined rules. |
| Cost | May lead to underutilization or over-provisioning of resources. | Optimizes costs by scaling based on demand. |
| Complexity | Requires manual intervention for scaling decisions. | Reduces management overhead with automated scaling. |
Monitoring and logging in Azure App Service
Monitoring and logging are crucial aspects of managing applications deployed on Azure App Service. They help in identifying issues, optimizing performance, and ensuring the overall health of the application.
Performance Monitoring Tools in Azure App Service
Azure App Service provides various monitoring tools to track the performance of applications. Some of the key tools include:
- Application Insights: Offers real-time monitoring, performance insights, and analytics to identify bottlenecks and optimize application performance.
- Azure Monitor: Provides a comprehensive monitoring solution for Azure resources, including Azure App Service, allowing you to track metrics, logs, and create alerts.
- Diagnostic Logs: Enable you to capture detailed information about requests, errors, and other events happening within the application.
Configuring Alerts in Azure App Service
To set up alerts based on specific metrics in Azure App Service, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the Azure portal and select your App Service instance.
- Go to the Monitoring section and choose Alerts.
- Click on New Alert Rule and select the desired metrics to monitor.
- Set the conditions for the alert trigger and configure the notification settings.
- Save the alert rule to start monitoring the specified metrics.
Custom Logging Configurations in Azure App Service
You can set up custom logging configurations for different components within an application by:
- Accessing the Application Settings of your Azure App Service instance.
- Adding or modifying the logging settings for the desired components, such as application code, web server, or database connections.
- Configuring the log levels, output format, and storage options based on your requirements.
Common Issues Identified Through Monitoring and Logging
Monitoring and logging in Azure App Service can help identify various common issues, such as:
- High response times or latency in application requests.
- Memory leaks or high CPU usage impacting performance.
- Errors in application code or dependencies causing failures.
Integrating Azure Monitor with Azure App Service
To integrate Azure Monitor with Azure App Service for comprehensive monitoring and logging capabilities:
- Access the Azure portal and navigate to the Azure Monitor section.
- Select the Azure App Service instance you want to monitor.
- Configure the monitoring settings, including metrics, logs, and alerts for the application.
- Enable the necessary diagnostics settings and set up data retention policies for long-term monitoring.
Custom domains and SSL in Azure App Service
When it comes to custom domains and SSL in Azure App Service, it’s essential to understand how to configure them properly to enhance branding and security measures for your application.
Configuring a Custom Domain
To configure a custom domain for your Azure App Service, follow these steps:
- Access the Azure portal and navigate to your App Service.
- Under Settings, select Custom Domains.
- Click Add Custom Domain and enter your domain name.
- Update the DNS records with your domain registrar to point to your Azure App Service.
- Verify the domain in the Azure portal to complete the configuration.
Obtaining and Installing SSL Certificates
To secure your Azure App Service with SSL certificates for HTTPS connections, consider these steps:
- Obtain an SSL certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority or through Azure Key Vault.
- Upload the SSL certificate to your Azure App Service under SSL settings.
- Update the binding for your custom domain to use the SSL certificate for secure connections.
- Verify the HTTPS connection to ensure the SSL certificate is properly installed.
Advantages of Custom Domains and SSL
Using custom domains and SSL in Azure App Service offers several advantages:
- Improved branding and user trust with a custom domain.
- Enhanced security measures with SSL certificates for encrypted connections.
- Compliance with industry standards and regulations for data protection.
- Better search engine rankings due to secure HTTPS connections.
Comparison Table: Default Domain vs. Custom Domain
| Aspect | Default Domain | Custom Domain |
|---|---|---|
| Branding | Uses azurewebsites.net domain | Uses your custom domain |
| Security | Shared SSL certificate | Dedicated SSL certificate for your domain |
| Trust | Generic domain may raise trust concerns | Custom domain builds trust with users |
Remember to keep your SSL certificates up to date and monitor your custom domain settings regularly for optimal performance and security.
Integration with Azure DevOps
Azure App Service offers seamless integration with Azure DevOps, providing a robust platform for continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) processes. This integration allows developers to automate deployments, streamline workflows, and enhance collaboration between development and operations teams.
Automate Deployments with Azure DevOps Pipelines
Azure DevOps Pipelines enable developers to automate the deployment process, ensuring efficient and consistent delivery of applications to Azure App Service. By defining build and release pipelines, teams can automate the deployment of code changes, run tests, and deploy applications to different environments with ease. This automation helps in reducing manual errors, increasing deployment speed, and maintaining a reliable release process.
- Set up build pipelines to compile code, run tests, and generate artifacts for deployment.
- Create release pipelines to deploy applications to Azure App Service, configure settings, and manage deployment approvals.
- Integrate with source control systems like GitHub or Azure Repos to trigger automated builds and deployments based on code changes.
Advantages of Integrating Azure App Service with Azure DevOps for CI/CD
Integrating Azure App Service with Azure DevOps offers several advantages for CI/CD processes, including:
- Streamlined Deployment: Automate the deployment process and ensure consistency across different environments.
- Collaboration: Facilitate collaboration between development and operations teams by enabling seamless integration and communication.
- Continuous Feedback: Receive real-time feedback on deployments, test results, and performance metrics to identify issues early and iterate quickly.
- Scalability: Scale applications easily with automated deployments and continuous delivery pipelines to meet changing business requirements.
Security features in Azure App Service
Azure App Service offers a range of built-in security features to help protect your applications and data from potential threats. Implementing authentication and authorization mechanisms is crucial to ensure secure access to your resources. Let’s explore the security features and best practices for securing applications deployed on Azure App Service.
Built-in Security Features
- Network Isolation: Azure App Service allows you to restrict access to your web applications by configuring network security groups and virtual network integration.
- Web Application Firewall: You can enable the Azure Web Application Firewall to protect your applications from common web vulnerabilities and attacks.
- SSL/TLS Encryption: Azure App Service supports SSL/TLS encryption to secure data in transit between clients and your web applications.
- Identity Management: Utilize Azure Active Directory integration for managing user identities and implementing single sign-on for your applications.
Implementing Authentication and Authorization
- To implement authentication, you can leverage Azure Active Directory, OAuth, or other identity providers supported by Azure App Service.
- For authorization, use role-based access control (RBAC) to define fine-grained permissions for accessing resources within your application.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security for user authentication.
Best Practices for Securing Applications
- Regularly update and patch your applications and dependencies to mitigate security vulnerabilities.
- Enable monitoring and logging to detect and respond to security incidents in a timely manner.
- Implement secure coding practices and perform security testing, such as penetration testing, to identify and address security weaknesses.
- Restrict access to sensitive data and resources based on the principle of least privilege.
Backup and disaster recovery in Azure App Service
In the event of a disaster, having a solid backup and recovery plan in place is crucial to ensure the continuity of your Azure App Service. Let’s dive into the steps to configure automated backups, the process of restoring a web app from a backup, and the different disaster recovery options available.
Configuring Automated Backups
To set up automated backups for your Azure App Service, follow these steps:
- Go to your Azure portal and navigate to your App Service.
- Under Settings, select Backups.
- Click on Configure.
- Choose the frequency, retention period, and storage account for your backups.
- Save your settings to enable automated backups for your web app.
Restoring a Web App from Backup
If you need to restore your web app from a backup, here’s how you can do it:
- Go to your Azure portal and navigate to your App Service.
- Under Settings, select Backups.
- Choose the backup you want to restore from and click Restore.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the restoration process.
Disaster Recovery Options
Here’s a comparison table outlining different disaster recovery options for Azure App Service:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Geo-replication | Replicates your app across different Azure regions for redundancy. |
| Azure Site Recovery | Provides automated failover and recovery for your app in case of a disaster. |
| Azure Backup | Offers backup and restore capabilities for your app data and configurations. |
Testing the Disaster Recovery Plan
To ensure the effectiveness of your disaster recovery plan, follow these steps:
- Simulate a disaster scenario to trigger the recovery process.
- Monitor the recovery process and verify that your app is restored successfully.
- Document any issues or improvements needed in your disaster recovery plan.
Performance optimization in Azure App Service
Azure App Service offers various strategies for optimizing performance to ensure your applications run smoothly and efficiently. By monitoring and improving performance, you can enhance user experience and reduce downtime. Let’s delve into some key aspects of performance optimization in Azure App Service.
Strategies for optimizing performance
- Utilize Azure Application Insights to monitor application performance and identify bottlenecks.
- Implement caching mechanisms to reduce load times and improve responsiveness.
- Optimize code and database queries to enhance overall application performance.
- Use Azure CDN to deliver content closer to users, reducing latency and improving speed.
Monitoring and improving performance
- Regularly monitor application performance metrics such as response time, CPU usage, and memory usage.
- Identify performance issues through tools like Azure Monitor and take proactive measures to address them.
- Scale your Azure App Service resources based on performance metrics to handle varying workloads efficiently.
Common performance issues and solutions
- High latency: Optimize network configurations and utilize CDN services to reduce latency.
- Overloaded servers: Implement auto-scaling to dynamically adjust resources based on demand.
- Poorly optimized code: Conduct code reviews and performance testing to identify and improve inefficient code sections.
- Database bottlenecks: Optimize database queries, use indexing, and consider database scaling options.
Cost management in Azure App Service
Azure App Service offers a flexible and scalable platform for hosting web applications, APIs, and mobile backends. However, managing costs effectively is crucial to optimizing your resources and maximizing value. Let’s explore the pricing model, tips for cost optimization, and strategies to avoid unexpected charges.
Pricing model for Azure App Service
Azure App Service offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, where you are charged based on the resources and features you use. The main factors that influence the cost include the selected service plan (such as Free, Shared, Basic, Standard, Premium, or Isolated), the number of instances, storage, bandwidth, and additional services like custom domains or SSL certificates. It’s important to monitor your usage regularly to understand how these factors impact your bill.
Tips for optimizing costs in Azure App Service
- Choose the right service plan: Select a service plan that aligns with your application’s requirements. Start with a lower-tier plan and scale up as needed to avoid overprovisioning.
- Utilize auto-scaling: Enable auto-scaling to automatically adjust the number of instances based on demand, helping you optimize resource utilization and reduce costs during periods of low traffic.
- Monitor and optimize resource usage: Regularly monitor your app’s performance metrics and adjust resources accordingly to avoid unnecessary expenses.
- Leverage Azure Reservations: Consider purchasing Azure Reservations for predictable workloads to benefit from discounted rates and cost savings.
Cost management strategies to avoid unexpected charges
- Set spending limits: Define budget thresholds and alerts to receive notifications when expenditures exceed predefined limits, helping you stay within budget.
- Utilize Azure Cost Management: Use Azure Cost Management and Billing to track, analyze, and optimize costs by identifying cost-saving opportunities and eliminating wasteful spending.
- Review and optimize Azure resources: Regularly review and optimize your Azure resources to identify unused or underutilized resources that can be removed or downsized to reduce costs.
- Implement tagging: Use resource tags to categorize and track costs by project, department, or environment, enabling better cost allocation and management.
Compliance and regulations in Azure App Service
Azure App Service is designed to meet various compliance certifications and regulations to ensure the security and privacy of data stored and processed within the platform. Compliance with industry standards is crucial for businesses that handle sensitive information and must adhere to specific rules and regulations.
Compliance Certifications and Regulations
Azure App Service complies with a range of certifications and regulations, including but not limited to:
- ISO 27001: Azure App Service adheres to the international standard for information security management systems, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
- GDPR: Azure App Service helps organizations comply with the General Data Protection Regulation by providing tools and features to manage data securely and transparently.
- HIPAA: Azure App Service meets the requirements of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, enabling healthcare organizations to store and process protected health information.
- PCI DSS: Azure App Service is compliant with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, ensuring that payment card data is handled securely.
Maintaining Compliance with Industry Standards
Azure App Service offers features such as data encryption, access control, and threat detection to help organizations maintain compliance with industry standards. By leveraging these security capabilities, businesses can protect sensitive information and mitigate the risk of data breaches or non-compliance penalties.
Importance of Compliance and Regulations
Compliance and regulations play a vital role in application development, especially when dealing with sensitive data or operating in regulated industries. By adhering to industry standards, organizations demonstrate their commitment to data protection, privacy, and security, building trust with customers and stakeholders. Failure to comply with regulations can lead to legal consequences, financial penalties, and reputational damage, highlighting the importance of maintaining compliance in all aspects of business operations.
High availability and redundancy in Azure App Service
Ensuring high availability and redundancy in Azure App Service is crucial for maintaining the reliability and performance of your applications. In this section, we will explore the features and strategies that Azure App Service offers to achieve this.
High availability features in Azure App Service
- Azure App Service provides built-in load balancing and automatic OS patching to reduce downtime and ensure application availability.
- It offers multi-region deployment options to distribute your application across different geographic locations for increased redundancy.
Setting up redundancy for applications
- To set up redundancy for applications deployed on Azure App Service, you can leverage features like Azure Traffic Manager to route traffic to healthy instances in case of failures.
- You can also configure auto-scaling based on predefined metrics to ensure that your application can handle fluctuations in traffic and workload.
Benefits of high availability and redundancy
- Increased uptime and reliability, reducing the risk of downtime and potential revenue loss.
- Improved performance and user experience by distributing workload and traffic effectively.
Configuring auto-scaling for high availability
- Step 1: Navigate to your Azure App Service resource in the Azure portal.
- Step 2: Go to the “Scale out (App Service Plan)” section and configure the auto-scaling settings based on your requirements.
Azure Traffic Manager for redundancy
- Azure Traffic Manager allows you to distribute traffic across multiple Azure regions to improve redundancy and fault tolerance.
- By setting up endpoints in different regions, you can ensure that users are always directed to the closest and healthiest instance of your application.
Azure Availability Zones vs. Azure Regional Pairs
| Criteria | Azure Availability Zones | Azure Regional Pairs |
|---|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Within a single region | Across two regions |
| Isolation | Physically separate data centers | Logical isolation within a region |
| Scalability | Enhanced scalability within a region | Scalability across regions |
Key metrics for maintaining high availability
- Response time: Monitor the response time of your application to identify performance issues.
- Downtime: Track the uptime of your application to ensure minimal disruptions.
- Resource utilization: Monitor CPU, memory, and storage utilization to optimize performance and scalability.
Advanced features of Azure App Service
Azure App Service offers a range of advanced features to enhance application development and deployment. Let’s dive into some of these advanced capabilities and how they can benefit your projects.
Deployment Slots
- Deployment slots allow you to create separate environments for testing, staging, and production without affecting your live application.
- Use cases: Test new features, perform A/B testing, and seamlessly swap between different versions of your app.
- To set up deployment slots in Azure App Service, navigate to the Azure portal, select your app service, and then click on “Deployment slots” to add a new slot.
Auto-Scaling
- Auto-scaling automatically adjusts the number of resources allocated to your app based on traffic patterns, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
- Benefits: Handle sudden traffic spikes, reduce downtime, and save costs by scaling resources up or down as needed.
Traffic Routing Strategies
- Azure App Service offers various traffic routing strategies, including weighted, performance, geographic, and priority-based routing.
- When to use each one: Weighted for A/B testing, performance for latency-sensitive applications, geographic for regional targeting, and priority for failover scenarios.
Pricing Plans
| Plan | Features |
|---|---|
| Free | Limited resources, shared infrastructure |
| Shared | Shared resources, custom domains, SSL support |
| Basic | Dedicated resources, auto-scaling, deployment slots |
| Premium | Advanced auto-scaling, traffic manager, custom domains |
Custom Domains Configuration
- To configure custom domains for Azure App Service, go to the Azure portal, select your app service, and navigate to “Custom domains” to add your custom domain.
- Benefits: Establish a branded online presence, improve SEO, and enhance trust with customers through a custom domain.
Monitoring and Performance Optimization
- Best practices for monitoring and optimizing performance include setting up application insights, analyzing performance metrics, and adjusting resources based on insights.
- Ensure proactive monitoring, identify and resolve performance bottlenecks, and continuously optimize your app for peak efficiency.
Future trends and developments in Azure App Service
Azure App Service has been at the forefront of cloud application development, offering a robust platform for developers to build, deploy, and scale web applications with ease. As technology continues to advance rapidly, it is essential to predict the future trends and developments in Azure App Service to stay ahead of the curve and meet the evolving needs of developers and organizations.
Predicted Trends in Cloud Application Development
- Increased focus on serverless computing to optimize resource utilization and reduce costs.
- Enhanced support for containerized applications to improve portability and scalability.
- Integration of AI and machine learning capabilities for intelligent automation and decision-making.
Potential Developments in Azure App Service
- Introduction of more advanced monitoring and logging features for better visibility and troubleshooting.
- Enhancements in security features to address emerging threats and compliance requirements.
- Integration with emerging technologies like IoT for seamless connectivity and data processing.
Evolution of Azure App Service
- Adoption of microservices architecture for improved modularity and scalability.
- Focus on hybrid cloud solutions to cater to diverse deployment needs and regulatory constraints.
- Continuous updates and optimizations to keep pace with industry standards and customer feedback.
Comparison with Other Cloud Application Platforms
- Advantages: Seamless integration with other Azure services, auto-scaling capabilities, and built-in DevOps support.
- Disadvantages: Limited customization options, dependency on Azure ecosystem, and potential cost implications.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
- AI: Integration of AI services for predictive analytics, chatbots, and personalized user experiences.
- IoT: Support for IoT devices and data processing to enable real-time insights and automation.
Roadmap for Enhancements in Azure App Service
Q3 2022: Release of enhanced security features
Q4 2022: Introduction of AI-driven automation tools
Q1 2023: Integration with IoT services for seamless connectivity
Summary
In conclusion, Azure App Service provides a robust solution for application development with seamless integration, auto-scaling capabilities, and enhanced security features. Stay ahead in the digital landscape with Azure App Service.